High user engagement correlates to high rankings
User experience may be the most underrated aspect of SEO, but when you look at SEMrush’s ranking factor study, it’s clear the impact that user engagement signals have on ranking performance.
There are several factors that are used when determining user engagement. Some of the most important when it comes to user satisfaction seems to be bounce rate, page procession, and time spent on site.
It is not 100 percent clear to us the extent that user satisfaction is taken into consideration by Google’s algorithms. What is clear is that Google has always been committed to keeping their users happy. This has been central to their strategy from day one. This is why most SEOs believe that good user experience equates to good SEO. This applies to Spanish SEO as well.
Mark Lopez, formerly Google’s head of U.S. Hispanic audience sales, told me once, “Do not think about what Google and Bing do. Think about what your Users want and you will be ahead of the game. Because most of what we do at Google is thinking what the User wants.”
My purpose in writing this article is to provide some tips on user experience/SEO optimization with the hopes of helping you improve your rankings. We are going to focus on two factors.
- How to increase time spent on site and keep your visitors around
- How to minimize bounce rate in 2021 by decreasing page load time
Get in touch with us, and then decide.
Hispanic Market Advisors helps you connect with the online Latino market and expand your reach.
Ways You Can Increase Time Spent on Site
When you sit down to create a strategy to improve on page SEO, one of the first questions you want to answer is how can you increase the amount of time a person spends on a page. You know that the longer a person spends on a page, the happier they are with the page and the more likely they are to convert into paying customers.
There are several factors that could influence the length of time a person spends on a page when it comes to SEO. For one thing, there is no clear-cut way to know what Google thinks is a sufficient amount of time for visitor to spend on a website for a given search query.
Think about This Example
A website might answer the question, what is 30 degrees Celsius in Fahrenheit? The answer to this question is straightforward. It does not require in-depth reading. In fact, if a user was forced to read through paragraphs of information to find the answer, they might get turned off and go elsewhere. Users will likely be happy with spending just a couple of seconds on a single page to get the answer to this question.
However, a user may search “What is the difference between a depression and an economic recession?” Now, the user is asking a question that is going to require some explaining on the part of the website. The user may need some time to thoroughly explore the topic. If a user visits a site that is supposed to answer a question like this but only stays on the site for a couple of seconds, it is a clear sign that the user is not satisfied with the site.
The goal is not necessarily to keep users on your website for X number of seconds. The goal is for users to want to explore your site for a sufficient amount of time to find the answers to queries that they have. You want users exploring your site as opposed to looking on the site of a competitor. Here is where the idea of supplementary content comes into play.
Pro Tip: Link to the Supplementary Content You Create
This is a great SEO practice. If you have a website that is focused on making craft beer, throughout your content you are going to include terms that are unique to this profession. For each term, you could link out to a blog or to another page on your site. If these links provide valuable information, users are going to expand their search by staying on your domain. This means they are not searching other domains for information that could theoretically lead them to your competition.
You see an excellent example of this when you look at a Wikipedia page. In just one paragraph, you will likely see links to half a dozen or more related topics. Each link directs you to a different Wikipedia page.
That being said, simply adding internal links on keywords that happen to be in the body of the text should not be considered the best way of referencing support content. There is a good example that we can learn from the website www.thebalance.com. On this site, you will notice that there are links to keywords in the body. However, the supplementary articles that they are linking to help the reader get a better grasp of the topic that is being discussed.
Each piece of content that is being linked to works to directly support the main article. You can imagine how beneficial this has to be for readers. They are going through an article and hit a topic that they are not familiar with. Many will choose to click on a link to find information that explains the term or topic they are not familiar with. Then, they will go back to the main article and likely repeat that same process several times. The result is that readers will spend more time on the same site because they are being provided with quality information.
Pro Tip: Answer Multiple Queries at the Same Time
We all have heard that it is better to kill two birds with one stone. The idea is that you achieve two objectives simultaneously.
For example, someone may want to know who the tallest person in the world is. It’s a fair guess that they would also be interested in knowing who the second tallest and the third tallest people are. They may be interested all the way up to the top 25. If they want to know who the tallest man is, they may be interested in knowing who the tallest woman is, who has the largest hands, who has the biggest feet, and who has the longest legs.
You can see examples of this when you look at the first two pages of the UK SERPs for the query, “What is the tallest building in the world?” The results do not just include information about the tallest building in the world. Instead, you see a list of at least five of the tallest buildings in the world.
All of this shows that when people make a search query, they are interested in value. They favor sites that have an intuitive value. It does more than offer the direct answer. It understands that people are interested in this topic, so it’s going to give information about this topic.
The interesting thing is that there are several websites, including Guinness World Record, that answer the direct question about the tallest building in the world. The answer is the Burj Khalifa just in case you were wondering.
What’s interesting is that articles that answer the direct question have been hidden by Google. For example, you can find the Guinness World Record site on page four in the SERPs. So what’s the point? People are looking for sites that anticipate the questions that they have or the questions they did not know that they had.
Your website can prove its value by anticipating subsequent searches and incorporating them into one piece of content. If a visitor lands on your page and they are greeted with more information than they expected to receive, it’s likely that they are going to stay on your page longer. This is going to make Google see your page as something that offers value. The longer your visitors consume your content, the higher chance you have of getting them to convert to whatever it is you want them to do.
Pro Tip: Showcase Related Content
As convenient as it is to bundle up all of the available information and stick it into one well written piece of content, you are not always going to be able to do this. This is a situation where you may benefit from creating related content and then including links to that related content.
There are several sites that do this well. One site that we appreciate is the BBC. When you visit the BBC’s website, you will see that they list articles related to a specific story. They also offer content that is relevant to the broader topic.
This strategy makes it possible for visitors to browse and find related content to the topic they are already reading on the same site. And what is interesting about this strategy is that it allows you to showcase content on your site that might be of interest to your readers that they had no idea existed on your site.
If you doubt the power of this strategy, just take a few minutes and think back to the last time you searched for a specific video on YouTube. Then, five hours later, you find yourself watching videos that you did not realize you would be interested in, would never have searched for, and did not know existed.
Basically, what YouTube is doing is taking the videos that you are currently watching and giving recommendations based on those. You click on the recommendation and then get more recommendations based on what you have already shown interest in. And it just goes on and on.
You see the same strategy when you visit an e-commerce site. Usually, on e-commerce sites the related content is other products that you might want to buy as opposed articles. And the listings are probably cookie-based and are personalized to you.
And while it’s true that sites like Amazon are providing a personalized shopping experience because they want you to buy more, you are going to be presented with products that are going to entice you to read more or purchase. Presenting you with products that you might be interested in even though you did not necessarily search for them keeps you on the site longer, which may make you spend more money.
Google sees a happy customer as one who sticks around to see what else there is on the site.
The importance of website engagement is a topic that has been discussed ad nauseam. We could add to the plethora of articles on the topic but would be writing for days, and this is beyond the scope of our article.
Instead, we are going to give you a few tips that can help improve the time spent on the site. We will also link out to articles that cover these topics.
- Navigation should be optimized and clear for all devices.
- The content should be scannable.
- Write content that is to the point. Do not include fluff.
- Include an internal search function.
- Make it easy to exit pop-ups.
Improve Page Speed and Tackle Bounce Rate
A comment on bounce rate.
When you read about bounce rate, you will see that it is a source of much controversy. In Google Analytics, when bounce rate is seen as a standalone metric, it shows the number of visitors who leave a web site after visiting just one page.
However, it’s not always a bad thing to leave a website after visiting just one page. For example, you might visit a site that gives immediate answers to specific queries. For example, you may want to know how many ounces of water are in a gallon. You visit the site and see the answer instantly.
You are not concerned about learning the formula for converting gallons to ounces. You just want your answer. A site like this is going to have a higher bounce rate than others. This shows that you shouldn’t make strategic SEO decisions based on bounce rate without having enough contextual information, including content type, calls to action, users intent, etc.
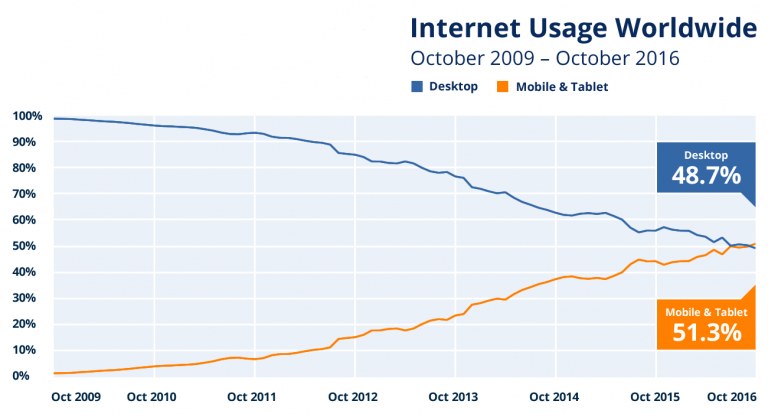
Since 2010, Google has made it clear that page speed is a factor in ranking. Moz and other authorities on the topic also indicate that this is the case. Additionally, in March 2017, Gary Illyes of Google said that page loading speed is a ranking factor of great importance in a mobile first world.
As of July 1, 2019, mobile first indexing is enabled by default on all new websites. Older websites need to make adjustments so that their users have the best experience, whether they are visiting from a desktop, PC, or mobile device. The point is that a website that loads quickly, whether it’s mobile or on a PC, is good for user experience and search engine optimization.
A fast loading website does not happen by accident. There are several aspects of your website you will need to control in order to get it to perform faster.
Use a Content Delivery Network
With a CDN, your content will be cached on multiple servers to serve visitors who are local quicker. CloudFlare is a great option used by many. However, there are other options that you can choose, including Akamai, MaxCDN, and Rackspace.
Use a Good Web Hosting Provider
This might require a little bit of work on your part. However, if you take the time to research good hosting companies, you can find one that will do miracles for your site when it comes to speed. You will especially notice a difference in time to first byte. You will be thankful that you took the time to read quality articles and research the subject.
Compress Images
Including large images is a surefire way to kill the page load time. There are several tools that can optimize image size while keeping visual quality.
- Tiny PNG
- JPEG Optimizer
- Compressor.io
- BJ Lazy Load
These are just a few of the amazing options available to you if you are looking to optimize and compress your images for faster loading times.
Take Advantage of Browser Caching
Browser caching makes it possible for browsers to remember loaded page elements. This makes it possible to speed up page load time for returning visitors. There is a lot of good information available on how you can implement this on your website.
Minify Resources
You can reduce the size of JavaScript, HTML, and CSS. There are several good articles that can help you along this path.
Obviously, you want to reduce bounce rate. However a low page load time can also increase conversion. Walmart is an excellent example of this. They were able to increase their conversion by two percent for every one second of page load speed improvement.
How do you check your site speed? Webpagetest.org is a great resource. It tells you how long it takes each element to load and then provides you with a score for each element. Some factors that are considered are:
- Effective Use of CDN
- First Byte Time
- Compress Transfer
- Keep Alive Enabled
- Cache Static Content
- Compress Images
It’s good to remember that the site speed is just one of many important aspects to consider when thinking about reducing bounce rate. There are several more. It’s good to read more articles on the subject to identify improvements that could minimize visitors bouncing.
Final Thoughts
User experience and SEO work as a team. If users are more satisfied with your site, it’s likely that you are going to have higher rankings. Of course, user experience is a broad subject. We were only able to provide a few tips to cover a small part of it.
My goal was to lay out some examples to pique your interest in user experience and hopefully help you come up with more ideas to improve the optimization of your website or the websites you are managing for clients.
Interested in Learning How to Add Spanish SEO into your Overall SEO Strategy?
Let us know by suggesting a date/time for a complimentary introductory call. If we feel we can help and there’s a match between your needs and our capabilities, we’ll then offer you with a Site Audit for you to get a picture of your current situation and map out possible solutions that work for you along with a proposal.
(* Booking Policy: If you don’t see your preferred time available on the calendar below you can send us an email at appointments@hispanicmarketadvisors.com.)
The journey of finding and fixing on-site issues and boosting your SEO for sustainable growth starts with your first step in the right direction.


Leave a Reply